Rosacea is a chronic skin condition that affects millions of people worldwide. Characterized by redness, visible blood vessels, and often small, red, pus-filled bumps on the face, rosacea can significantly impact both physical appearance and emotional well-being. While the exact cause remains unclear, understanding its triggers and effective management strategies can help individuals live more comfortably with this condition.
What is Rosacea?
Rosacea is a chronic inflammatory skin condition that most commonly affects the central face, including the cheeks, nose, forehead, and chin. It typically appears in cycles, with periods of flare-ups followed by remission. While it is most common in fair-skinned individuals aged 30–50, rosacea can affect people of all skin tones and ages.
Key Symptoms Include:
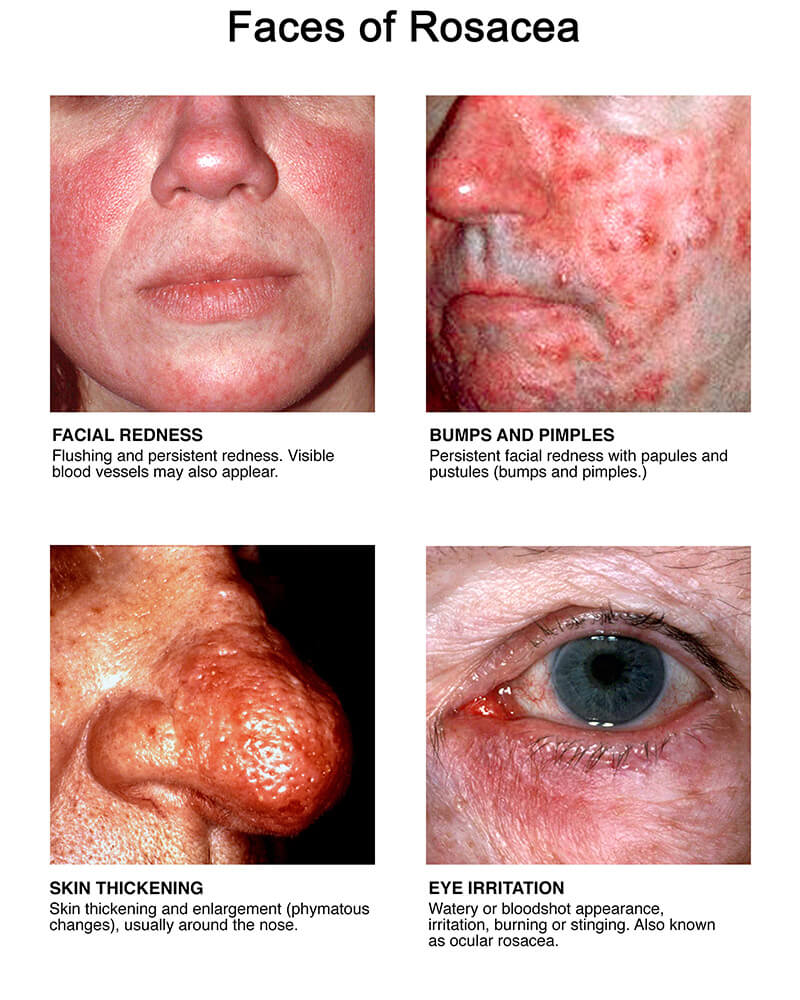
- Persistent facial redness
- Visible blood vessels (telangiectasia)
- Small, red bumps that may resemble acne
- Burning or stinging sensations
- Thickened skin, especially on the nose (in severe cases, called rhinophyma)
- Eye irritation (ocular rosacea)
What Causes Rosacea?
The exact cause of rosacea is not fully understood, but research points to several contributing factors:
-
Immune System Dysregulation:
Rosacea may involve an overactive immune response that leads to chronic inflammation. -
Genetics:
A family history of rosacea increases the likelihood of developing the condition. -
Microbial Imbalance:
An overgrowth of Demodex mites, naturally occurring microorganisms on the skin, has been associated with rosacea flares. -
Environmental and Lifestyle Factors:
External factors such as sun exposure, stress, and extreme weather conditions can exacerbate symptoms.
Common Triggers of Rosacea
Identifying and avoiding personal triggers is a cornerstone of managing rosacea. While triggers can vary, some of the most common include:
- Sun Exposure: UV radiation can worsen redness and inflammation.
- Heat and Cold: Extreme temperatures or rapid changes can irritate the skin.
- Dietary Triggers: Spicy foods, hot drinks, alcohol (especially red wine), and caffeine may provoke flare-ups.
- Stress and Emotional Factors: Stress and anxiety often exacerbate symptoms.
- Skincare Products: Harsh cleansers, alcohol-based products, and fragrances can irritate sensitive skin.
- Physical Exertion: Intense exercise or overheating during workouts may cause flushing.
Rosacea Subtypes
Rosacea is categorized into four main subtypes based on its presentation:
- Erythematotelangiectatic Rosacea (ETR): Persistent redness, flushing, and visible blood vessels.
- Papulopustular Rosacea: Red bumps and pustules resembling acne, often accompanied by redness.
- Phymatous Rosacea: Thickened, bumpy skin, particularly on the nose.
- Ocular Rosacea: Eye irritation, dryness, or visible blood vessels around the eyes.
Effective Management Strategies
Managing rosacea requires a multifaceted approach, combining lifestyle modifications, skincare, and medical treatments.
-
Lifestyle Adjustments:
- Avoid Triggers: Keep a diary to track potential triggers and avoid them whenever possible.
- Sun Protection: Wear a broad-spectrum sunscreen (SPF 30 or higher) daily and seek shade during peak sunlight hours.
- Manage Stress: Incorporate stress-reduction techniques such as meditation, yoga, or therapy.
-
Skincare Routine:
- Gentle Cleansing: Use a mild, non-foaming cleanser to avoid stripping the skin.
- Moisturize Regularly: Hydrating the skin helps maintain its barrier function and reduce sensitivity.
- Avoid Irritants: Choose fragrance-free and alcohol-free products designed for sensitive skin.
- Topical Treatments: Prescription medications such as metronidazole, azelaic acid, or ivermectin creams can reduce inflammation and redness.
-
Dietary Modifications:
- Minimize consumption of known dietary triggers, such as alcohol and spicy foods.
- Include anti-inflammatory foods like leafy greens, fatty fish, and berries to support overall skin health.
-
Medical Treatments:
For moderate to severe rosacea, dermatological interventions may be necessary:- Laser and Light Therapies: Treatments such as intense pulsed light (IPL) or vascular lasers can reduce redness and visible blood vessels.
- Oral Medications: Antibiotics like doxycycline may be prescribed for their anti-inflammatory effects.
- Isotretinoin: In rare cases, this medication is used for severe, treatment-resistant rosacea.